
An Introduction to Surround Systems
What is Surround Sound
Surround sound is a multi-directional sound enrichment technique that uses multiple audio channels distributed between loudspeakers that surround the listener. It debuted in movie theaters but has spread to wider commercial and home use due to increased affordability and breadth of product offerings. Surround sound adds one or more channels from loudspeakers to the side or behind the listener that are able to create the sensation of sound coming from any horizontal direction around the listener.
The technique enhances the perception of sound spatialization by exploiting sound localization: a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. This is achieved by using multiple discrete audio channels routed to an array of loudspeakers. Surround sound typically has a listener location (sweet spot) where the audio effects work best and presents a fixed or forward perspective of the sound field to the listener at this location.
Commercial surround sound media include videocassettes, DVDs, and SDTV broadcasts encoded as analog matrixed Dolby Surround compressed Dolby Digital and DTS, and lossless audio such as DTS HD Master Audio and Dolby TrueHD on HDTV Blu-ray Disc and HD DVD, which are identical to the studio master. Other commercial formats include the competing DVD-Audio (DVD-A) and Super Audio CD (SACD) formats, and MP3 Surround. Cinema 5.1 surround formats include Dolby Digital and DTS. Sony Dynamic Digital Sound (SDDS) is an 8-channel cinema configuration that features 5 independent audio channels across the front with two independent surround channels, and a Low-frequency effects channel. Traditional 7.1 surround speaker configuration introduces two additional rear speakers to the conventional 5.1 arrangement, for a total of four surround channels and three front channels, to create a more 360° sound field.
What is a Surround Sound System comprised of
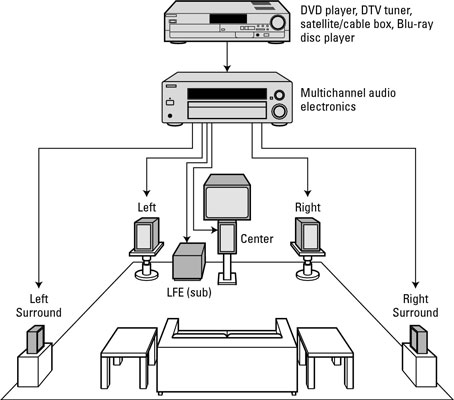
Surround sound formats vary in reproduction and recording methods, along with the number and positioning of additional channels. Prior to surround sound, theater sound systems commonly had three screen channels of sound that played from three loudspeakers situated left, center, and right at the front of the audience. The center speaker channel is primarily important for delivering the base front-facing audio, which is considered to be the majority of audio effects that one expects to hear.
The most common surround sound specification, the International Telecommunications Union's (ITU) 5.1 standard, calls for 6 channels and thus 6 speakers: center (C), in front of the listener; left (L) and right (R), at angles of 60°; left surround (LS) and right surround (RS) at angles of 100–120°; and a subwoofer, whose position is not critical. A subwoofer provides the famous bass effect that adds depth and tactility to audio. Meanwhile, the 7.1, 9.1, and 11.1 standards boast 8 channels, 10 channels and 12 channels respectively.
A surround sound system's speakers and subwoofer are controlled and regulated by a control device with built in amplifier. This device is either a A/V receiver or a soundbar. A soundbar plays its own discrete audio while also passing the audio signal to other surround speakers and the subwoofer either wired or wirelessly so that they also play supporting surround audio in real time. In contrast, an A/V receiver does not play audio, but rather relies on its onboard drivers and specialized electrical components to optimize the audio quality for the speakers it passes its enhanced audio signal to. As a result, the A/V receiver is able to produce a significantly higher quality audio feed than any soundbar.
Components List
- Pair of front side speakers
- Front center speaker
- Pair of surround side speakers
- Pair of rear or height speakers
- Subwoofer
- Soundbar or A/V Receiver
- HDMI cable
- Speaker wire
- optical or coaxial digital audio cables
- RCA cable or adapter
Qualities and Features of Surround Sound
When we think of interior design, we often overlook ambient sound. This brings us to the centerpiece of our discussion today — the surround sound system. This remarkable innovation has transformed our engagement with sound and in this blog, we’ll delve into the benefits of surround sound systems.
A surround sound system can:
- provide ambient and harmonious noise for relaxation .
- replicate the immersive sound of nature for meditation
- play music tracks in high fidelity quality for a luxurious lounge experience
- create a lively and convivial atmosphere for social gatherings and house dining
- set up a premium and immersive entertainment experience for movies and games
- enhance garage band music performances
Room Shapes and Sizes Impact Sound
The geometric shape profile, size, and construction materials of a room can have a major impact on sound quality. Larger rooms can lead to echo and uneven sound distribution, while smaller, square rooms may experience problematic room modes that cause uneven bass. Hard surfaces reflect sound, creating echoes, whereas soft materials absorb sound, reducing reverberation. Optimizing acoustics involves balancing absorption and reflection, and addressing potential issues like standing waves and room modes through acoustic treatment
Tips for Budgeting
To build a surround sound system on a budget:
- focus on quality over quantity, prioritize essential components, and consider buying open-box or refurbished items from reputable dealers, which often come with warranties and are significantly cheaper. If you have the opportunity, be sure to test used equipment befor purchasing
- set a firm budget and determine a realistic spending limit and stick to it. Prioritize essential components like the receiver, front speakers, and subwoofer. Consider building the system gradually, buying components as you can afford them
- explore brands known for offering good value for money, such as Monoprice, Fluance, or Polk Audio. Refer to our Trusted Brands page for a comprehensive directory of audio equipment directly from major brands' stores
- read reviews and compare specifications to find the best options within your budget
- a 2.1 system (left, right, and subwoofer) is a great starting point and can be expanded to a 5.1 or 7.1 system later as budget allows. Allocate a significant portion of your budget to the front three speakers (left, right, and center) as they are crucial for the immersive experience
- consider a soundbar with Dolby Atmos support if you need a more affordable space-saving solution.
- the receiver is the heart of the system, so choose one with enough power and features for your needs. Look for features like Dolby Atmos if you plan to upgrade to Atmos speakers later. Invest in quality left, right, and center front speakers, as they handle the majority of the sound. Also select a good subwoofer which adds depth and impact to the low frequencies, enhancing the overall experience
- consider the acoustics of your room as well as future upgrade paths when choosing speakers and placement. For example, choose a receiver with enough power and inputs to accommodate future expansion
